 |
| GIS Application |
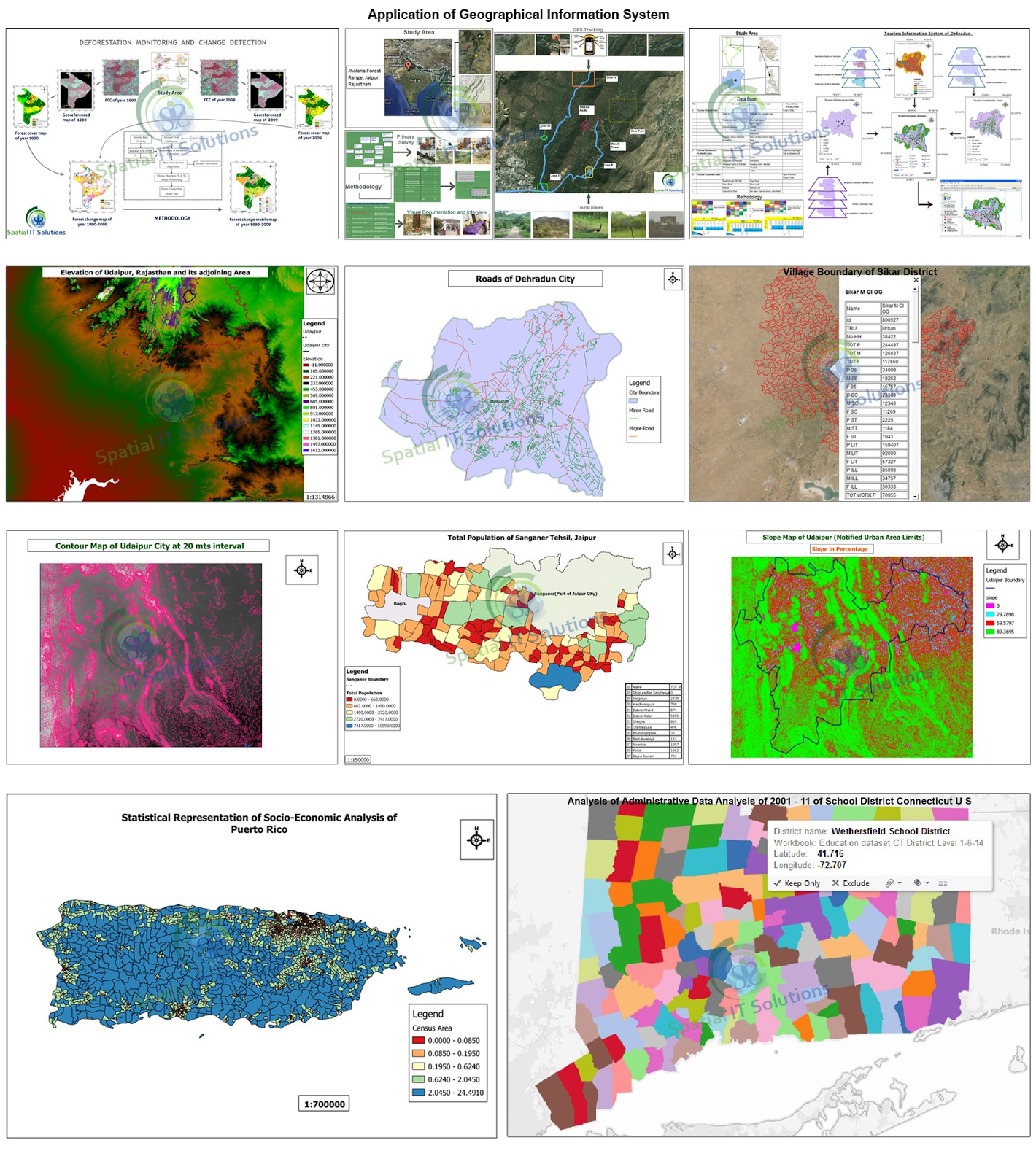
GIS is a technique or an information system that provides spatial information within and outside the planet earth. It is one of the best ways to explore as it gives the integrate information about the attributes in every field. It mainly gives information about the geographical data through map that are also in digital form.
To make a better use of GIS it in important to know about the application and the use of GIS in its field like business, transport, tourism etc.
There are 5 major applications used in diverse field which are as follows:
To make a better use of GIS it in important to know about the application and the use of GIS in its field like business, transport, tourism etc.
There are 5 major applications used in diverse field which are as follows:
1. Facilities management
2. Natural resource management
3. Transport network
4. Planning and engineering
5. Land information system
i) Business
ii) Agriculture
2. Natural resource management
3. Transport network
4. Planning and engineering
5. Land information system
i) Business
ii) Agriculture
1. Facilities management- Large scale and precise maps and network analysis are used mainly for utility management. Automated mapping/facility management is frequently used in this area.
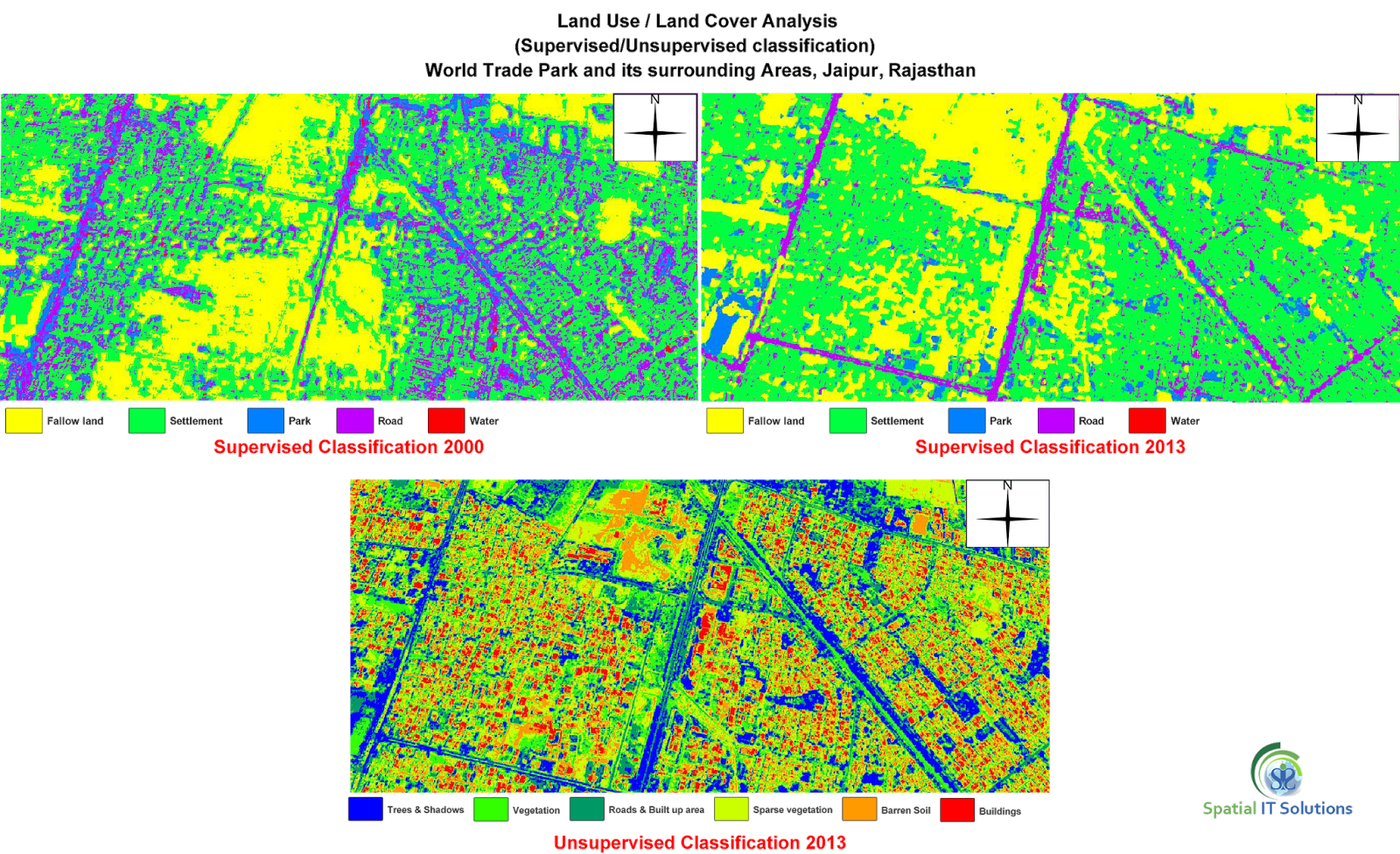
2. Natural resource management- It is an overlay technique and maps with scales of medium and small that shows the combination of aerial photographs and satellite images which are used for natural resource management.
3. Transport network- Maps of large or medium scale and spatial analysis are used for the purpose of networking,location of streets etc.
4. Planning and Engineering- Engineering models along with large and medium scale maps are mainly used in civil engineering.
5. Land information system- Large scale Cadastre maps or land parcel maps and spatial analysis are used for Cadastre administration, taxation etc.
i) Business- GIS is a tool that helps in locating things and managing the business through tracing the business sites and customers.
ii) Agriculture- GIS application is used in agricultural field that shows the yield of crops,species,region,soil etc.
Other than 5 major applications along with agriculture and business application some more important applications are environment, geology, hydrology, mapping, military, forestry, etc. Therefore, there are numerous aspects and advantages to gather new and important information through GIS in diverse field to make a better decision.
2. Natural resource management- It is an overlay technique and maps with scales of medium and small that shows the combination of aerial photographs and satellite images which are used for natural resource management.
3. Transport network- Maps of large or medium scale and spatial analysis are used for the purpose of networking,location of streets etc.
4. Planning and Engineering- Engineering models along with large and medium scale maps are mainly used in civil engineering.
5. Land information system- Large scale Cadastre maps or land parcel maps and spatial analysis are used for Cadastre administration, taxation etc.
i) Business- GIS is a tool that helps in locating things and managing the business through tracing the business sites and customers.
ii) Agriculture- GIS application is used in agricultural field that shows the yield of crops,species,region,soil etc.
Other than 5 major applications along with agriculture and business application some more important applications are environment, geology, hydrology, mapping, military, forestry, etc. Therefore, there are numerous aspects and advantages to gather new and important information through GIS in diverse field to make a better decision.