 |
| What is Image Classification? |
Remote sensing is the science and the art of obtaining information about an object, area, or phenomenon through the analysis of data acquired by a device that is not contact with the object, area or phenomenon under investigation.(Lillesand and Kiefer, 1994). The images taken are in the form of pixel and the process of changing it into digital images that make sense is known as image classification.It is based on technique that provides information through images. For eg.Land cover futher categorised into- forest,water,agriculture etc.
The two basic classifications are:
- Supervised
- Unsupervised
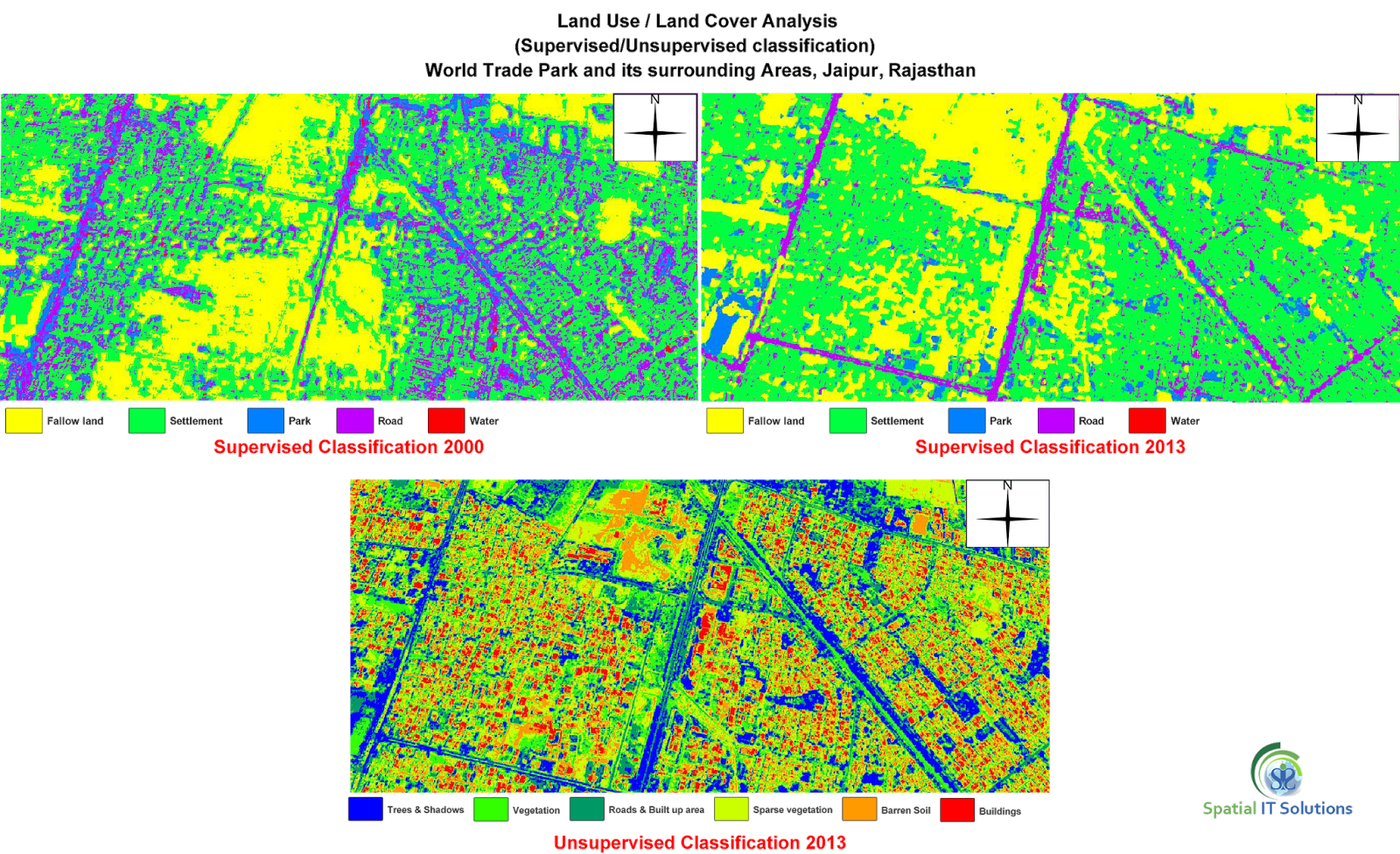
1. Supervised- This classification requires "training sites" where a person is aware about the ground so that a polygon can be digitized of that area.The image processing software system is then used to develop a statistical characterization of the reflectance for each information class. This stage is often called "signature analysis" and may involve developing a characterization as simple as the mean or the rage of reflectance on each bands, or as complex as detailed analyses of the mean, variances and covariance over all bands.(Eastman, 1995)
Supervised classification is further classified into:
- Parallelpiped
- Minimum distance to mean
- Maximum likelihood
2. Unsupervised- Unsupervised classification is a method which examines a large number of unknown pixels and divides into a number of classed based on natural groupings present in the image values. unlike supervised classification, unsupervised classification does not require analyst-specified training data. The basic premise is that values within a given cover type should be close together in the measurement space (i.e. have similar gray levels), whereas data in different classes should be comparatively well separated (i.e. have very different gray levels) (PCI, 1997; Lillesand and Kiefer, 1994; Eastman, 1995 )
Unsupervised is further classified into technique:
- K-Means classification
- SODATA classification
- Expectation Maximization (EM)classification